Welcome to the comprehensive guide to incomplete and codominance worksheet answer key. This guide will provide a detailed overview of the concepts of incomplete dominance and codominance, along with their inheritance patterns and real-world applications. By the end of this guide, you will have a thorough understanding of these important genetic principles.
Incomplete Dominance
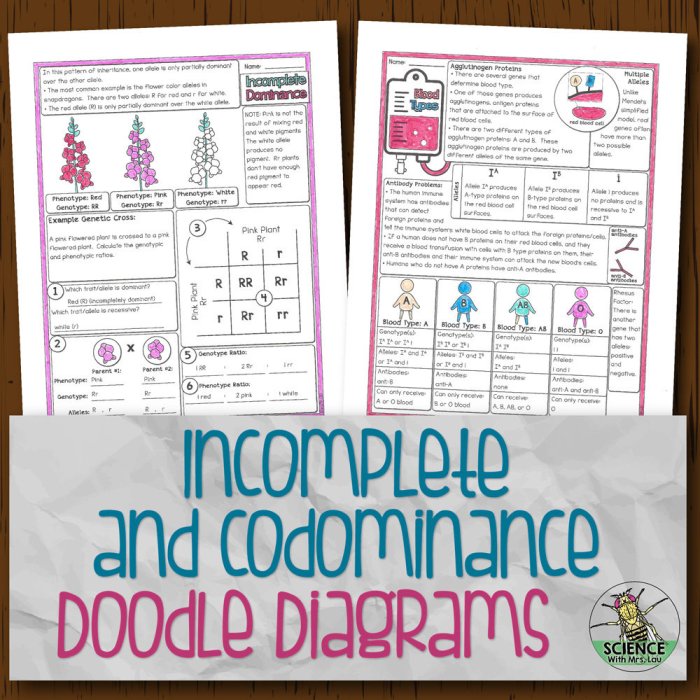
Incomplete dominance occurs when neither allele in a heterozygous genotype is fully dominant over the other. As a result, the phenotype of the heterozygote is a blend of the phenotypes of the two homozygotes.
Examples of incomplete dominance include:
- Snapdragons: When a red snapdragon is crossed with a white snapdragon, the offspring are pink.
- Andalusian horses: When a black horse is crossed with a white horse, the offspring are gray.
The inheritance pattern of incomplete dominance is as follows:
- Homozygous dominant (RR): Red snapdragons
- Heterozygous (RW): Pink snapdragons
- Homozygous recessive (WW): White snapdragons
Codominance
Codominance occurs when both alleles in a heterozygous genotype are fully expressed. As a result, the phenotype of the heterozygote is a combination of the phenotypes of the two homozygotes.
Examples of codominance include:
- Human blood types: The A and B alleles for blood type are codominant. As a result, individuals with the AB blood type have both A and B antigens on their red blood cells.
- Roan horses: The black and white alleles for coat color are codominant. As a result, roan horses have a coat that is a mixture of black and white hairs.
The inheritance pattern of codominance is as follows:
- Homozygous dominant (AA): Blood type A
- Heterozygous (AB): Blood type AB
- Homozygous recessive (BB): Blood type B
Worksheet Answer Key: Incomplete And Codominance Worksheet Answer Key
| Question | Answer | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| What is the phenotype of a heterozygous snapdragon? | Pink | Incomplete dominance occurs when neither allele is fully dominant, resulting in a blended phenotype. |
| What is the genotype of a roan horse? | Bb | Codominance occurs when both alleles are fully expressed, resulting in a combination phenotype. |
| What is the blood type of a person with the AB genotype? | AB | Codominance occurs when both alleles are fully expressed, resulting in a combination phenotype. |
Punnett Square Analysis
Punnett squares can be used to predict the genotypes and phenotypes of offspring in incomplete dominance and codominance crosses.
To construct a Punnett square, write the genotypes of the parents along the top and side of the square.
For example, if we cross a red snapdragon (RR) with a white snapdragon (WW), the Punnett square would look like this:
| R | R | |
|---|---|---|
| W | RW | RW |
| W | RW | RW |
The Punnett square shows that all of the offspring will be heterozygous (RW) and have a pink phenotype.
Real-World Applications
Incomplete dominance and codominance have practical applications in fields such as agriculture, medicine, and forensics.
In agriculture, incomplete dominance can be used to create new varieties of plants with desirable traits.
For example, farmers have used incomplete dominance to create new varieties of wheat with increased resistance to disease.
In medicine, codominance can be used to identify genetic disorders.
For example, the AB blood type is codominant, which means that people with the AB blood type have both A and B antigens on their red blood cells.
In forensics, codominance can be used to identify individuals from DNA evidence.
For example, the HLA system is a group of genes that are codominant.
This means that each individual has two HLA alleles, one inherited from each parent.
FAQs
What is incomplete dominance?
Incomplete dominance is a genetic phenomenon in which neither allele of a gene is dominant over the other. As a result, the heterozygous genotype exhibits a phenotype that is intermediate between the phenotypes of the two homozygous genotypes.
What is codominance?
Codominance is a genetic phenomenon in which both alleles of a gene are expressed in the phenotype of the heterozygous genotype. As a result, the heterozygous genotype exhibits a phenotype that is distinct from both homozygous genotypes.
How can I use Punnett squares to predict the genotypes and phenotypes of offspring in incomplete dominance and codominance crosses?
Punnett squares are a useful tool for predicting the genotypes and phenotypes of offspring in incomplete dominance and codominance crosses. To use a Punnett square, first write the genotypes of the parents along the top and side of the square.
Then, fill in the squares with the possible genotypes of the offspring. The genotypes of the offspring can be determined by multiplying the alleles of the parents in each square. The phenotypes of the offspring can be determined by using the incomplete dominance or codominance rules.