Exercise 9 review sheet the axial skeleton – The axial skeleton, a vital component of our body’s framework, plays a crucial role in protecting, supporting, and facilitating movement. Embark on an exploration of this essential structure, unraveling its anatomy, functions, and clinical significance.
The axial skeleton, comprising the skull, vertebral column, and rib cage, safeguards delicate organs, provides structural support, and enables a wide range of movements. Understanding its intricate workings deepens our appreciation for the remarkable complexity of the human body.
Anatomy of the Axial Skeleton
The axial skeleton is the central portion of the human skeleton, consisting of the bones that form the skull, vertebral column, and rib cage. It provides protection, support, and facilitates movement for the body.
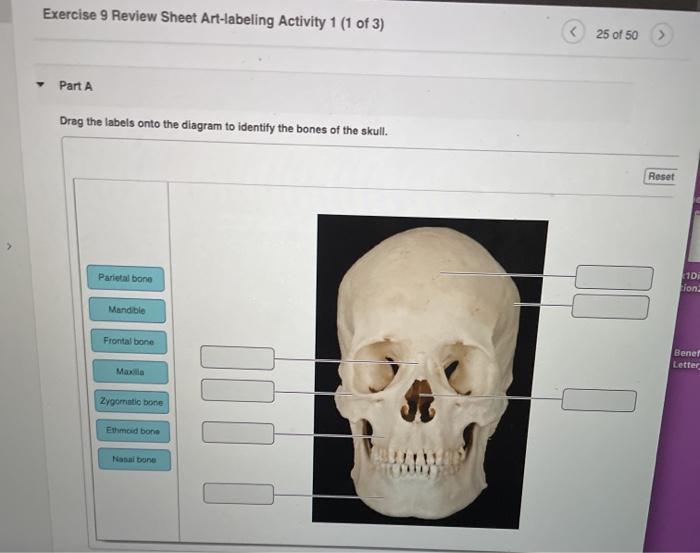
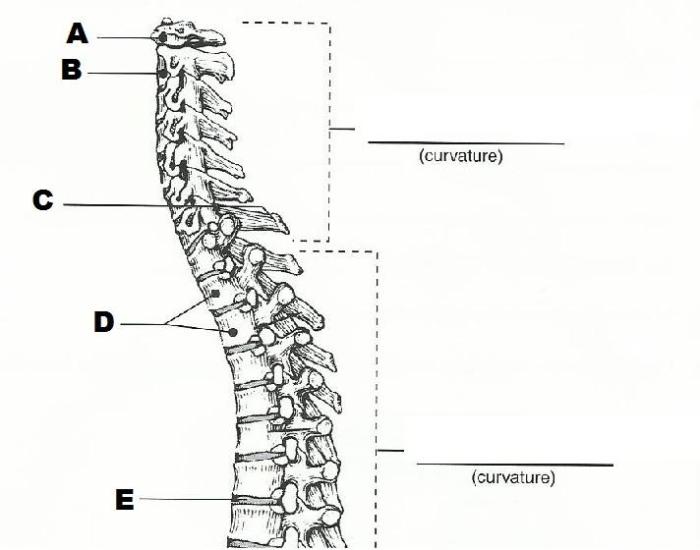
The skull, composed of 22 bones, encloses and protects the brain and sensory organs. The vertebral column, made up of 33 vertebrae, supports the head, provides flexibility, and houses the spinal cord. The rib cage, formed by 24 ribs and the sternum, protects the heart and lungs, and assists in respiration.
Functions of the Axial Skeleton, Exercise 9 review sheet the axial skeleton
The axial skeleton serves multiple crucial functions:
- Protection:It shields vital organs such as the brain, spinal cord, heart, and lungs from injury.
- Support:It provides a framework for the body, enabling it to stand upright and perform various movements.
- Movement:The vertebrae and ribs facilitate movement of the head, neck, and trunk.
Detailed FAQs: Exercise 9 Review Sheet The Axial Skeleton
What are the main functions of the axial skeleton?
The axial skeleton primarily serves three key functions: protection of vital organs, provision of structural support for the body, and facilitation of movement.
What are the common injuries associated with the axial skeleton?
Common injuries affecting the axial skeleton include skull fractures, spinal cord injuries, and rib fractures. These injuries can result from trauma, falls, or accidents.
How is the axial skeleton protected from damage?
The axial skeleton is protected by various mechanisms, including the skull, which encloses and safeguards the brain; the vertebrae, which shield the spinal cord; and the rib cage, which protects the heart and lungs.