Signal transduction pathways pogil answers provide a profound understanding of the intricate mechanisms that govern cellular communication and response. Embark on a journey to decipher the components, types, regulation, and applications of these pathways, unlocking the secrets of intercellular signaling.
Delve into the depths of signal transduction pathways, exploring their fundamental concepts and diverse roles in biological processes. Gain insights into the regulation of these pathways, unraveling the intricate feedback mechanisms that maintain cellular homeostasis.
Signal Transduction Pathways: Signal Transduction Pathways Pogil Answers
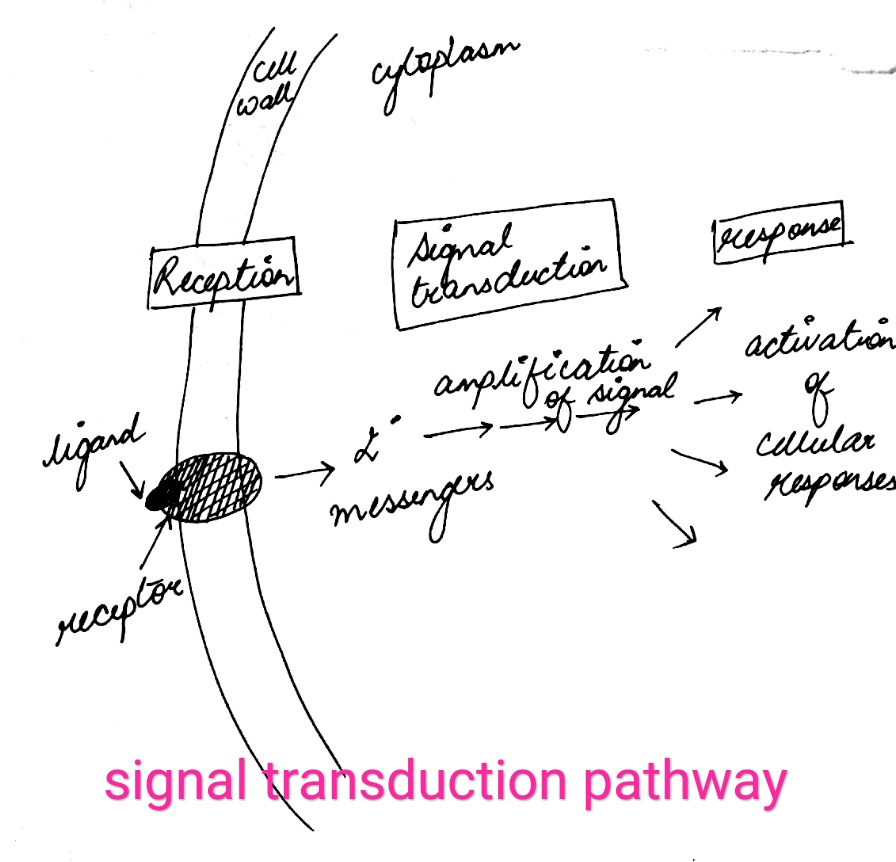
Signal transduction pathways are intricate networks of molecules that relay signals from the outside of a cell to the inside, enabling cells to respond to their environment and regulate cellular activities. These pathways involve a series of sequential steps, each involving specific molecules that interact to transmit the signal.
Components Involved in Signal Transduction Pathways
- Ligands: Molecules that bind to receptors, initiating the signal transduction cascade.
- Receptors: Proteins that bind to ligands and undergo conformational changes to activate downstream signaling events.
- Signal Transducers: Proteins that transmit the signal from the receptor to the nucleus or other intracellular targets.
- Effectors: Proteins that produce the final response to the signal, such as gene transcription or protein synthesis.
Examples of Signal Transduction Pathways
- MAPK pathway: Involved in cell growth, differentiation, and stress response.
- PI3K pathway: Regulates cell metabolism, growth, and survival.
- Jak-STAT pathway: Involved in cytokine signaling and immune responses.
Types of Signal Transduction Pathways
Receptor Tyrosine Kinase (RTK) Pathways
Involve receptors with tyrosine kinase domains that phosphorylate downstream targets.
G Protein-Coupled Receptor (GPCR) Pathways, Signal transduction pathways pogil answers
Utilize GPCRs that activate heterotrimeric G proteins, which then regulate effectors.
Ion Channel-Linked Pathways
Involve ligand-gated ion channels that directly alter the flow of ions across the membrane.
Jak-STAT Pathways
Emphasize the role of Janus kinases (Jaks) and signal transducers and activators of transcription (STATs) in signal transmission.
Regulation of Signal Transduction Pathways
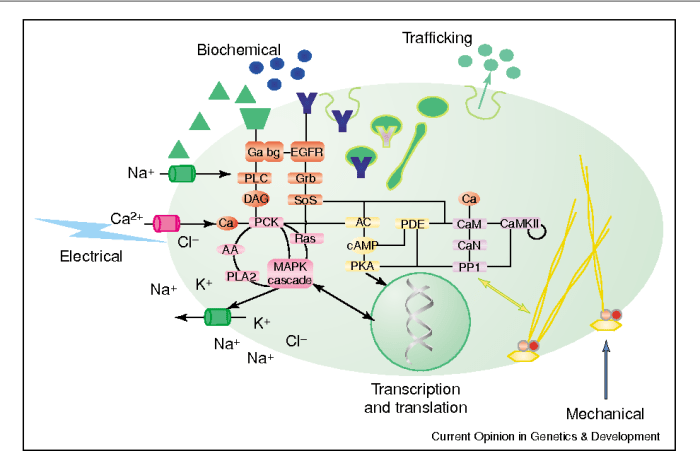
Signal transduction pathways are tightly regulated to ensure appropriate cellular responses and prevent aberrant signaling.
Feedback Mechanisms
- Negative feedback: Inhibits the pathway to prevent overstimulation.
- Positive feedback: Amplifies the signal to enhance the response.
Other Regulatory Mechanisms
- Ligand availability
- Receptor expression
- Signal transducer modifications
Applications of Signal Transduction Pathways
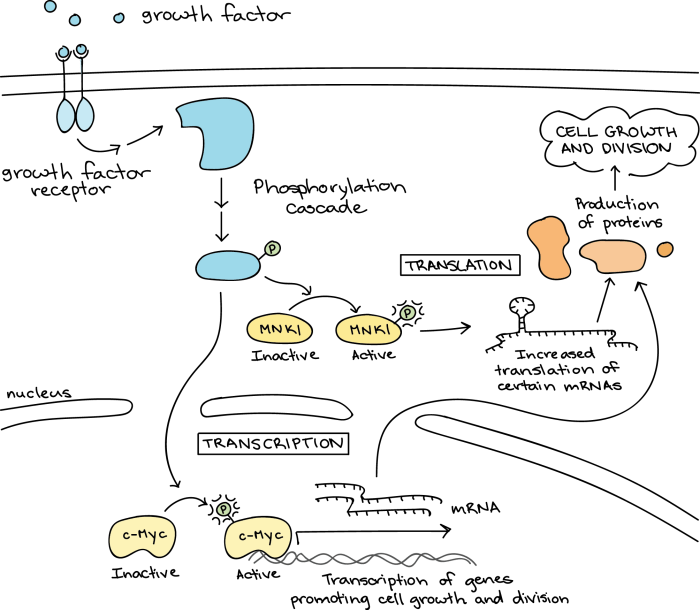
Drug Development
Targeting signal transduction pathways has led to the development of drugs for various diseases, such as cancer and immune disorders.
Disease Diagnosis
Alterations in signal transduction pathways can serve as biomarkers for disease diagnosis and prognosis.
Therapeutic Applications
- Inhibition of overactive pathways in cancer
- Activation of dormant pathways to enhance immune responses
FAQ Explained
What is the significance of signal transduction pathways?
Signal transduction pathways are essential for coordinating cellular responses to external stimuli, enabling cells to communicate, adapt, and maintain homeostasis.
How are signal transduction pathways regulated?
Signal transduction pathways are tightly regulated through feedback mechanisms, ensuring appropriate and timely cellular responses.
What are the potential therapeutic applications of targeting signal transduction pathways?
Targeting signal transduction pathways holds immense promise for developing novel therapies for various diseases, including cancer and immune disorders.