The atomic basics worksheet answer key provides a comprehensive guide to understanding the fundamental building blocks of matter. Delving into the depths of atomic structure, properties, and reactions, this key unlocks the secrets of the atom, empowering students with a deeper comprehension of the microscopic world.
This detailed resource encompasses the essential concepts of atomic physics, including the structure of atoms, the arrangement of electrons, and the relationships between atomic properties. It explores the various types of chemical bonds, explaining how atoms interact to form molecules and compounds.
Furthermore, it delves into nuclear reactions, their applications, and safety concerns.
Atomic Structure
An atom is the basic unit of matter and consists of a nucleus and electrons. The nucleus is located at the center of the atom and contains protons and neutrons. Protons have a positive charge, while neutrons have no charge.
Electrons are negatively charged particles that orbit the nucleus in specific energy levels.
Nucleus
The nucleus is composed of protons and neutrons. The number of protons in the nucleus determines the atomic number of the atom, which identifies the element. The number of neutrons determines the isotope of the element. Isotopes of the same element have the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons.
Electron Arrangement
Electrons are arranged in energy levels around the nucleus. The first energy level can hold up to two electrons, the second energy level can hold up to eight electrons, and so on. The electrons in the outermost energy level are called valence electrons and determine the chemical properties of the atom.
Atomic Properties
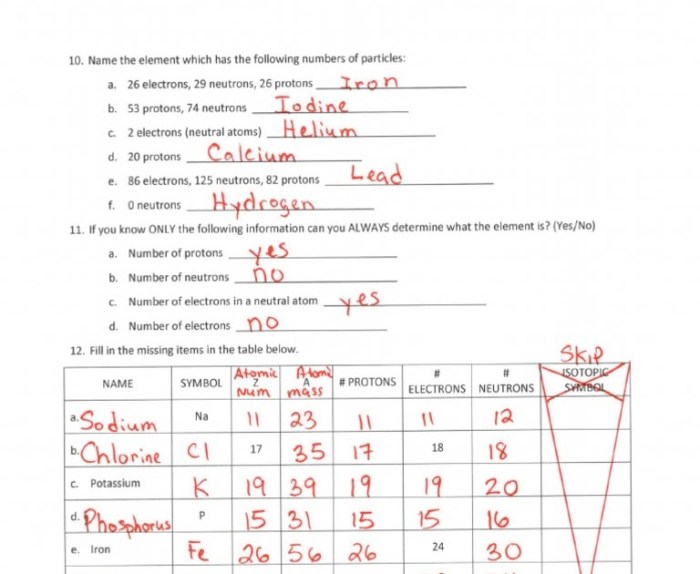
Atomic Number and Mass Number
The atomic number of an atom is the number of protons in the nucleus. The mass number of an atom is the sum of the number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus.
Calculating Number of Protons, Neutrons, and Electrons
To calculate the number of protons, neutrons, and electrons in an atom, use the following formulas:
- Number of protons = atomic number
- Number of neutrons = mass number – atomic number
- Number of electrons = atomic number
Relationship to Periodic Table
The atomic number and mass number of an atom determine its position on the periodic table. Elements with similar chemical properties are grouped together in the same column, while elements with increasing atomic number are arranged in rows.
Chemical Bonding

Types of Chemical Bonds
Chemical bonds are the forces that hold atoms together to form molecules and compounds. There are three main types of chemical bonds:
- Ionic bonds: Formed between atoms that transfer electrons, resulting in positively charged ions and negatively charged ions.
- Covalent bonds: Formed when atoms share electrons, creating a strong bond between the atoms.
- Metallic bonds: Formed between metal atoms that share electrons in a sea of delocalized electrons.
Interaction of Atoms, Atomic basics worksheet answer key
Atoms interact to form molecules and compounds by combining their valence electrons. The number and arrangement of valence electrons determine the type of chemical bond that forms.
Electronegativity
Electronegativity is the ability of an atom to attract electrons. The more electronegative an atom, the more strongly it attracts electrons. Electronegativity influences the type and strength of chemical bonds.
Nuclear Reactions
Definition and Types
Nuclear reactions are processes that involve changes in the structure of atomic nuclei. There are two main types of nuclear reactions:
- Nuclear fission: The splitting of a heavy nucleus into two or more lighter nuclei.
- Nuclear fusion: The combining of two or more light nuclei into a heavier nucleus.
Applications
Nuclear reactions have various applications, including:
- Energy production in nuclear power plants
- Medical imaging techniques like PET and MRI
- Production of radioactive isotopes for medical and industrial uses
Safety Concerns
Nuclear reactions can also pose safety concerns, such as:
- Release of radioactive materials into the environment
- Nuclear waste disposal
- Potential for nuclear accidents
Applications of Atomic Physics: Atomic Basics Worksheet Answer Key
Medicine
Atomic physics plays a crucial role in medical advancements:
- Radiation therapy for cancer treatment
- Radioactive isotopes for medical imaging and diagnosis
- Development of new drugs and treatments
Materials Science
Atomic physics contributes to the development and understanding of materials:
- Nanotechnology and nanomaterials
- Semiconductors and electronic devices
- Superconductivity and energy storage
Energy
Atomic physics is essential for energy production and research:
- Nuclear power plants
- Renewable energy sources like solar and wind
- Development of new energy technologies
Future Applications
Atomic physics continues to drive advancements in various fields:
- Quantum computing and information processing
- Artificial intelligence and machine learning
- Space exploration and astrophysics
Helpful Answers
What is the purpose of an atomic basics worksheet?
An atomic basics worksheet is designed to reinforce understanding of the fundamental concepts of atomic physics, such as atomic structure, properties, and reactions.
How does the answer key help students?
The answer key provides correct responses to the worksheet questions, enabling students to check their understanding, identify areas for improvement, and enhance their overall knowledge.
What are the benefits of using an atomic basics worksheet answer key?
Utilizing an atomic basics worksheet answer key allows students to:
- Verify their answers and identify errors.
- Reinforce their understanding of atomic physics concepts.
- Prepare effectively for assessments and exams.