Identify the irreversible reactions of glycolysis under intracellular conditions – The irreversible reactions of glycolysis under intracellular conditions play a pivotal role in the directionality and efficiency of this fundamental metabolic pathway. This comprehensive exploration delves into the identification, significance, regulation, and clinical implications of these reactions, providing a thorough understanding of their crucial contribution to cellular energy production.
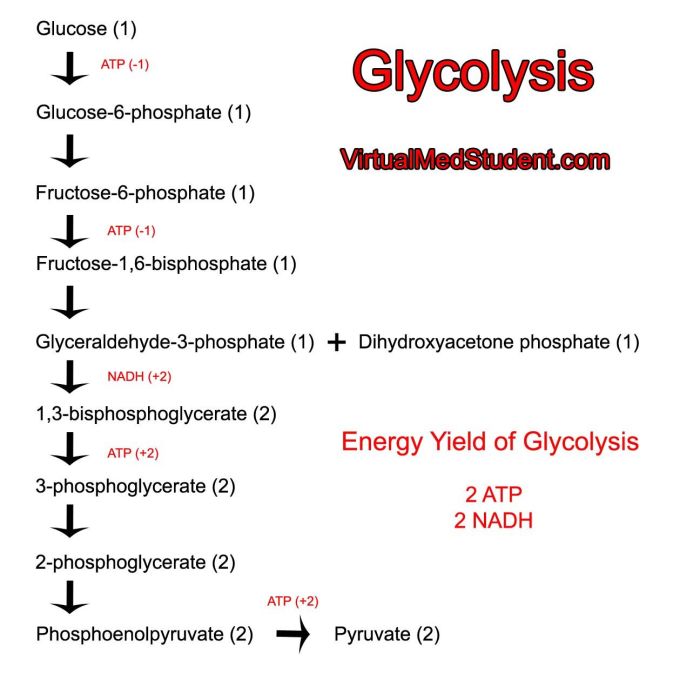
Glycolysis, the initial stage of cellular respiration, is a sequence of ten enzymatic reactions that convert glucose into pyruvate. Among these reactions, three stand out as irreversible: the phosphorylation of glucose by hexokinase, the isomerization of fructose-6-phosphate to fructose-1,6-bisphosphate by phosphofructokinase-1, and the dephosphorylation of 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate to 3-phosphoglycerate by phosphoglycerate kinase.
Irreversible Reactions in Glycolysis: Identify The Irreversible Reactions Of Glycolysis Under Intracellular Conditions
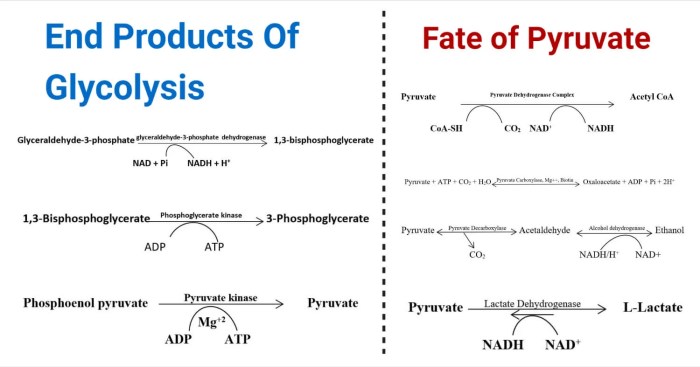
Glycolysis, the initial phase of cellular respiration, involves a series of ten enzymatic reactions that convert glucose into two molecules of pyruvate. Among these reactions, three are irreversible under intracellular conditions: the phosphorylation of glucose by hexokinase, the conversion of fructose-6-phosphate to fructose-1,6-bisphosphate by phosphofructokinase-1 (PFK-1), and the dephosphorylation of phosphoenolpyruvate to pyruvate by pyruvate kinase.
Importance of Irreversible Reactions, Identify the irreversible reactions of glycolysis under intracellular conditions
The irreversibility of these reactions is crucial for maintaining the directionality of glycolysis and preventing the backward flow of metabolites. Irreversible reactions create metabolic checkpoints that ensure the progression of glycolysis in a forward direction, preventing the accumulation of intermediate metabolites and ensuring the efficient utilization of glucose.
Regulation of Irreversible Reactions
The activity of irreversible reactions in glycolysis is tightly regulated by a combination of hormonal and allosteric factors. Hormones such as insulin and glucagon can influence the activity of PFK-1, while allosteric effectors like ATP, ADP, and citrate can modulate the activity of hexokinase and pyruvate kinase.
Consequences of Irreversible Reactions
Inhibiting irreversible reactions in glycolysis can have significant consequences. Blocking hexokinase can lead to the accumulation of glucose in the blood, while inhibiting PFK-1 or pyruvate kinase can disrupt the production of pyruvate and energy.
Clinical Implications
Defects in irreversible reactions of glycolysis can lead to metabolic disorders. For example, a deficiency in hexokinase can cause hemolytic anemia, while a deficiency in pyruvate kinase can result in pyruvate kinase deficiency anemia.
Commonly Asked Questions
What are the irreversible reactions of glycolysis?
The irreversible reactions of glycolysis are the phosphorylation of glucose by hexokinase, the isomerization of fructose-6-phosphate to fructose-1,6-bisphosphate by phosphofructokinase-1, and the dephosphorylation of 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate to 3-phosphoglycerate by phosphoglycerate kinase.
Why are irreversible reactions important in glycolysis?
Irreversible reactions are important in glycolysis because they prevent the backward flow of metabolites and ensure the unidirectional flow of the pathway, which is crucial for the efficient production of energy.
How are irreversible reactions regulated in glycolysis?
Irreversible reactions in glycolysis are regulated by various mechanisms, including hormonal and allosteric factors, which influence the activity of key enzymes involved in these reactions.