The brain parts involved in the fight or flight response crossword is a captivating exploration of the intricate mechanisms that govern our body’s response to stress and danger. This article delves into the roles of the amygdala, hypothalamus, and hippocampus in triggering and regulating the fight or flight response, providing a comprehensive understanding of this essential survival mechanism.
The fight or flight response is a complex physiological and behavioral reaction that prepares the body to confront or flee from perceived threats. Understanding the brain structures involved in this response is crucial for comprehending how our bodies and minds respond to stress and adversity.
Brain Parts Involved in the Fight or Flight Response
The fight or flight response is a physiological reaction that occurs in response to perceived threats or danger. It involves a complex interplay of various brain regions that work together to prepare the body for action.
Amygdala, Brain parts involved in the fight or flight response crossword
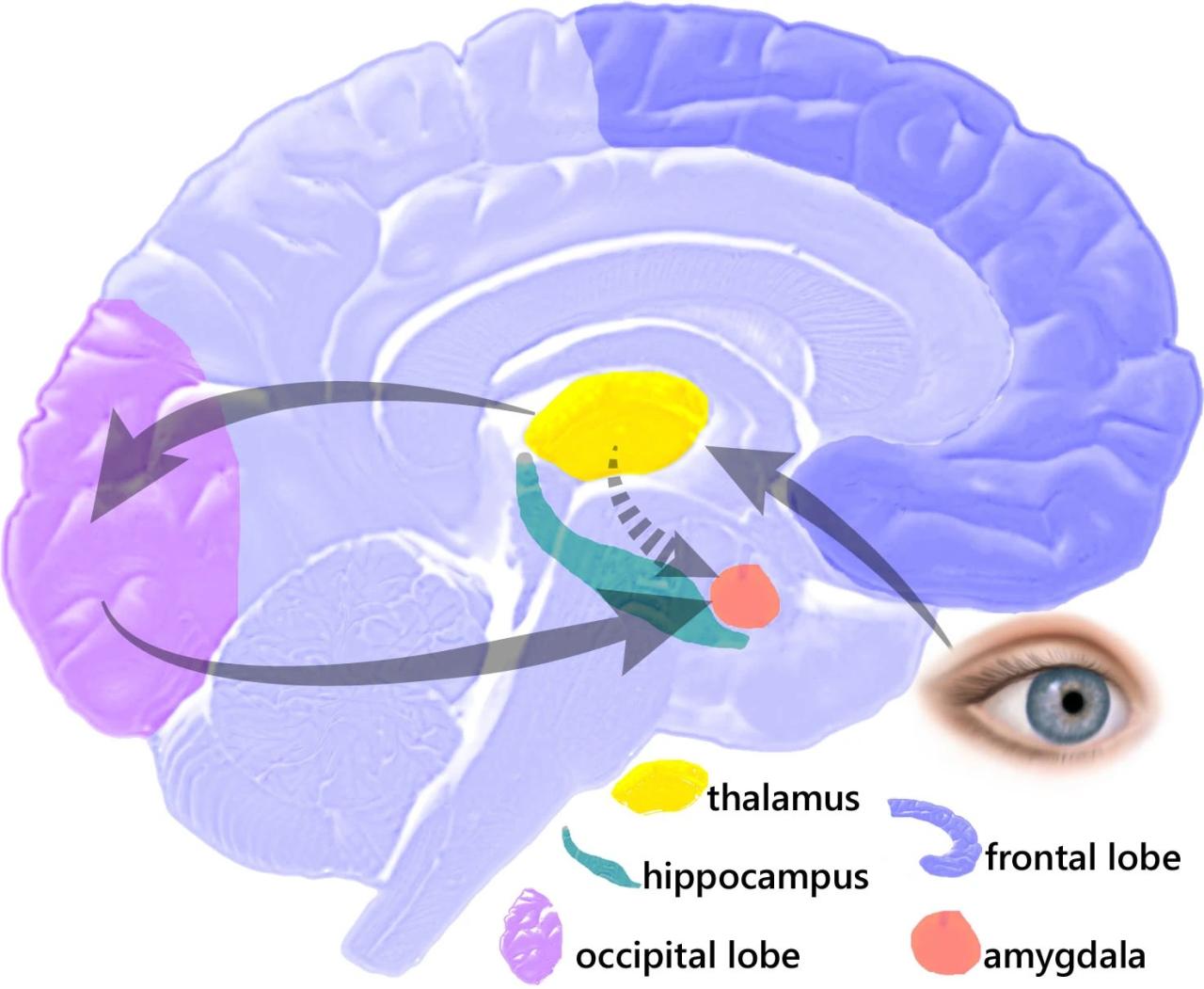
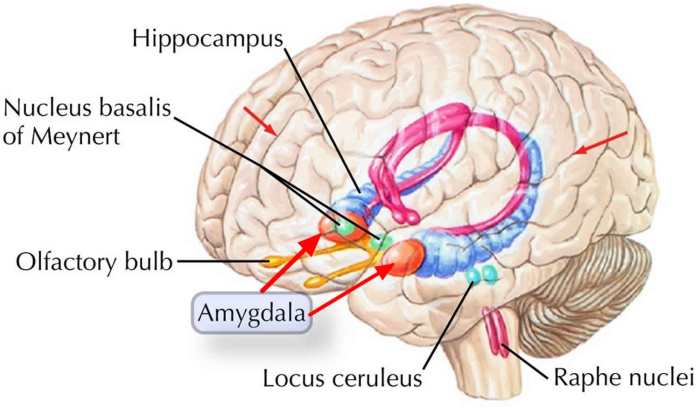
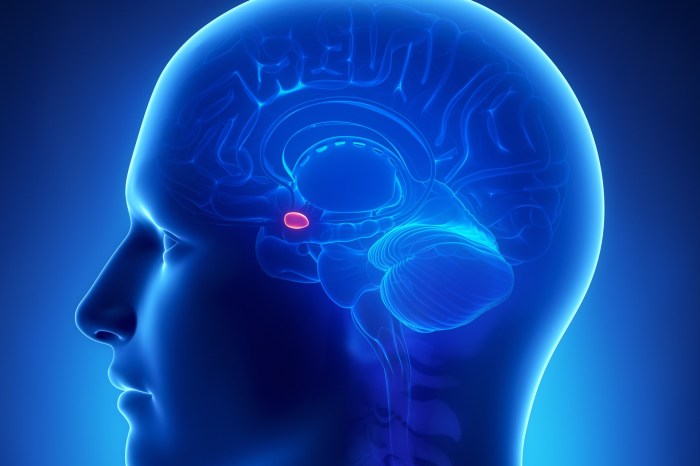
The amygdala is a small, almond-shaped structure located deep within the brain. It is responsible for processing emotional stimuli and plays a crucial role in triggering the fight or flight response. When a potential threat is detected, the amygdala sends signals to other brain regions to initiate the physiological and behavioral changes associated with the response.
Hypothalamus
The hypothalamus is a small region of the brain located at the base of the skull. It is involved in regulating a wide range of bodily functions, including stress responses. When the amygdala triggers the fight or flight response, the hypothalamus releases hormones such as cortisol and adrenaline, which prepare the body for physical action.
Hippocampus
The hippocampus is a brain structure located in the medial temporal lobe. It is involved in memory and emotional processing. During the fight or flight response, the hippocampus helps to consolidate memories of the threatening event and to regulate the emotional response associated with it.
Physiological Changes During the Fight or Flight Response: Brain Parts Involved In The Fight Or Flight Response Crossword
The fight or flight response is characterized by a number of physiological changes that prepare the body for physical action. These changes include:
- Increased heart rate and respiration
- Elevated blood pressure
- Dilation of pupils
- Increased muscle tension
- Diversion of blood flow to the muscles
- Release of stress hormones
These physiological changes are mediated by the sympathetic nervous system, which is activated in response to the threat signal from the amygdala. The sympathetic nervous system releases hormones such as adrenaline and cortisol, which have a variety of effects on the body, including increasing heart rate, blood pressure, and muscle tension.
Cognitive and Behavioral Responses to the Fight or Flight Response
The fight or flight response also involves a number of cognitive and behavioral changes. These changes include:
- Heightened awareness
- Focused attention
- Increased vigilance
- Aggression
- Avoidance
- Escape
These cognitive and behavioral changes are mediated by the prefrontal cortex, which is responsible for higher-order cognitive functions such as planning and decision-making. The prefrontal cortex helps to regulate the fight or flight response and to promote adaptive coping mechanisms.
Maladaptive Responses to the Fight or Flight Response
While the fight or flight response is a normal and adaptive response to threat, it can become maladaptive if it is chronically activated. Chronic activation of the fight or flight response can lead to a number of negative consequences, including:
- Anxiety
- Depression
- Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD)
- Insomnia
- Cardiovascular disease
- Gastrointestinal problems
These maladaptive responses can disrupt daily functioning and impair mental health. It is important to learn how to manage and regulate the fight or flight response in a healthy manner.
Commonly Asked Questions
What is the role of the amygdala in the fight or flight response?
The amygdala is a small almond-shaped structure located deep within the brain that plays a critical role in triggering the fight or flight response. It is responsible for detecting potential threats and initiating the body’s immediate response to danger.
How does the hypothalamus regulate the hormonal response to stress?
The hypothalamus is a small region at the base of the brain that serves as a central regulator of the body’s hormonal responses. During the fight or flight response, the hypothalamus releases hormones such as cortisol and adrenaline, which prepare the body for action.
What is the involvement of the hippocampus in memory and emotional processing during the fight or flight response?
The hippocampus is a brain structure that plays a crucial role in memory and emotional processing. During the fight or flight response, the hippocampus helps to consolidate memories associated with the perceived threat, which can influence future responses to similar situations.
