Build a two dimensional crystal of sodium chloride – Delving into the captivating realm of crystallography, we embark on an exploration of the intricate world of sodium chloride crystals. From their fundamental structure to their diverse applications, we unravel the fascinating properties and significance of these ubiquitous ionic compounds.
The face-centered cubic crystal structure of sodium chloride, with its alternating arrangement of sodium and chloride ions, forms the foundation of our investigation. We delve into the electrostatic forces that govern their interactions, shaping the crystal’s stability and properties.
Crystal Structure of Sodium Chloride
Sodium chloride (NaCl) crystallizes in a face-centered cubic (fcc) crystal structure. In this structure, sodium ions (Na+) and chloride ions (Cl-) are arranged in a repeating pattern of alternating layers. Each sodium ion is surrounded by six chloride ions, and each chloride ion is surrounded by six sodium ions.
Arrangement of Ions
The fcc structure of sodium chloride can be visualized as a cube with sodium ions at each corner and in the center of each face. The chloride ions are located in the center of each edge of the cube and in the center of the cube itself.
Building a Two-Dimensional Crystal Model
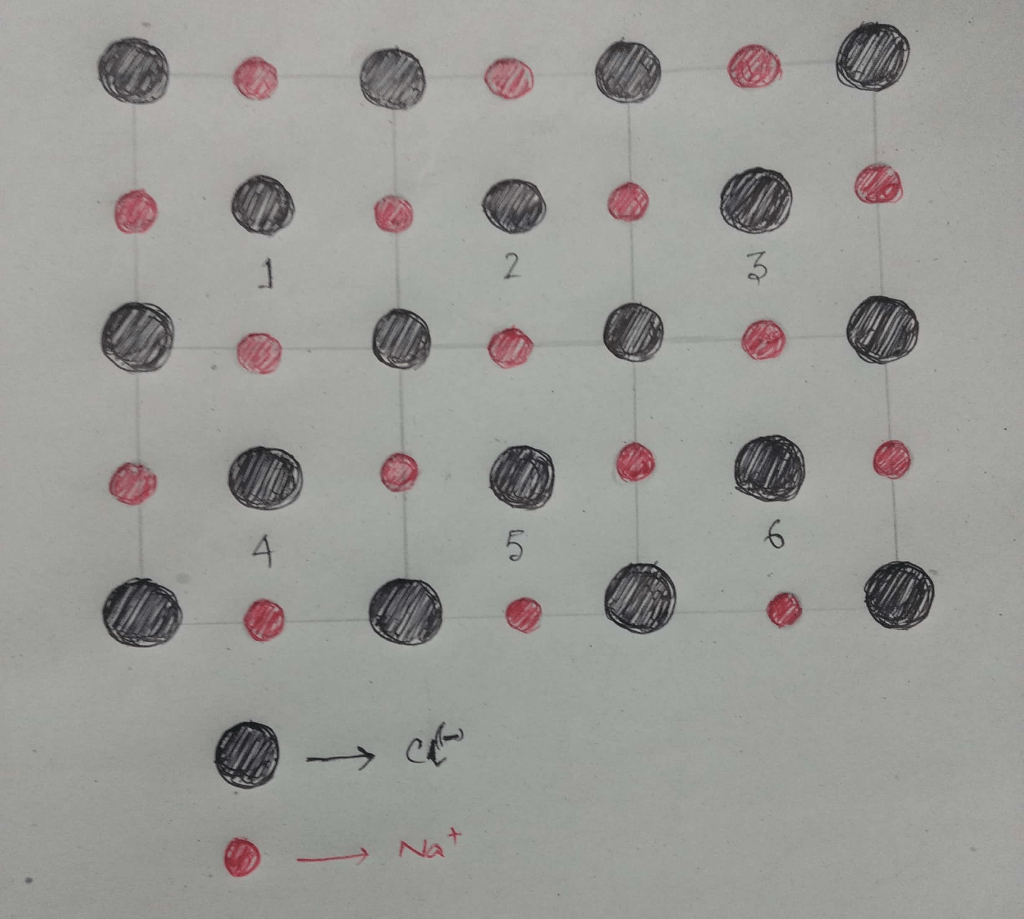
Using Physical Materials
To build a two-dimensional crystal model of sodium chloride using physical materials, you will need:
- White beads (sodium ions)
- Green beads (chloride ions)
- Toothpicks or straws
- Glue
Follow these steps:
- Arrange the white beads in a square.
- Place a green bead in the center of each side of the square.
- Place a toothpick or straw between each white bead and each green bead.
- Glue the toothpicks or straws in place.
Using Digital Tools, Build a two dimensional crystal of sodium chloride
To build a two-dimensional crystal model of sodium chloride using digital tools, you can use a modeling software program such as ChemDraw or Avogadro.
Follow these steps:
- Open the modeling software program.
- Create a new document.
- Draw a square.
- Place a circle in the center of each side of the square.
- Connect the circles to each other with lines.
Bonding in Sodium Chloride
The bonding in sodium chloride is ionic. This means that the sodium atoms lose one electron each to become sodium ions (Na+), and the chlorine atoms gain one electron each to become chloride ions (Cl-).
The oppositely charged ions are attracted to each other by electrostatic forces, forming a strong ionic bond.
Properties of Sodium Chloride Crystals
Sodium chloride crystals have a number of physical and chemical properties, including:
- Melting point: 801°C
- Boiling point: 1465°C
- Solubility in water: 35.7 g/100 mL
- Electrical conductivity: Good
Applications of Sodium Chloride Crystals

Sodium chloride crystals have a variety of applications, including:
- Food preservation
- Water purification
- Industrial processes
Sodium chloride is also used as a seasoning and flavor enhancer in food.
Comparison to Other Crystal Structures
The crystal structure of sodium chloride is similar to the crystal structures of other alkali halides, such as potassium chloride (KCl) and rubidium chloride (RbCl).
However, the crystal structure of sodium chloride is different from the crystal structures of other common materials, such as diamond and graphite.
Diamond has a diamond cubic crystal structure, in which each carbon atom is surrounded by four other carbon atoms in a tetrahedral arrangement.
Graphite has a hexagonal crystal structure, in which each carbon atom is surrounded by three other carbon atoms in a planar arrangement.
FAQ Section: Build A Two Dimensional Crystal Of Sodium Chloride
What is the significance of the face-centered cubic structure of sodium chloride?
The face-centered cubic structure maximizes the packing efficiency of sodium and chloride ions, resulting in a stable and energetically favorable arrangement.
How does ionic bonding contribute to the properties of sodium chloride crystals?
Ionic bonding, involving the electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions, imparts strength, rigidity, and high melting and boiling points to sodium chloride crystals.
What are some practical applications of sodium chloride crystals?
Sodium chloride crystals find widespread use in food preservation (as table salt), water purification, and various industrial processes, such as the production of chlorine and sodium hydroxide.