Embark on a comprehensive journey through the intricacies of accounting with our meticulously crafted Accounting 201 Final Exam Cheat Sheet. Designed to empower you with a solid foundation, this guide delves into the core concepts, principles, and practices that will equip you for success in your final exam and beyond.
Throughout this cheat sheet, we will explore the fundamental building blocks of accounting, including its underlying concepts and principles. We will delve into the significance of adhering to accounting standards and illustrate how these principles are applied in real-world scenarios.
Accounting Concepts and Principles
Accounting concepts and principles are the foundation of accounting. They provide a framework for accountants to follow when preparing financial statements. The most important accounting concepts include the going concern concept, the matching principle, and the accrual basis of accounting.
Accounting standards are important because they ensure that financial statements are consistent and reliable. This allows users of financial statements to compare the financial performance of different companies.
Examples of How Accounting Principles Are Applied in Practice
- The going concern concept assumes that a company will continue to operate in the foreseeable future. This assumption is used to justify the recording of assets at their historical cost rather than at their current market value.
- The matching principle requires that expenses be matched to the revenues they generate. This principle ensures that a company’s financial statements reflect its true economic performance.
- The accrual basis of accounting requires that transactions be recorded when they occur, regardless of when cash is received or paid. This principle ensures that a company’s financial statements reflect its true financial position.
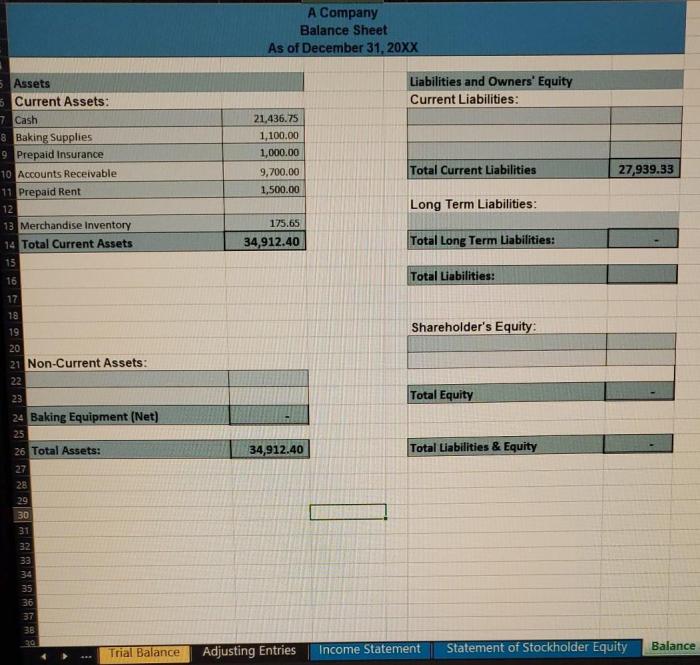
Financial Statements
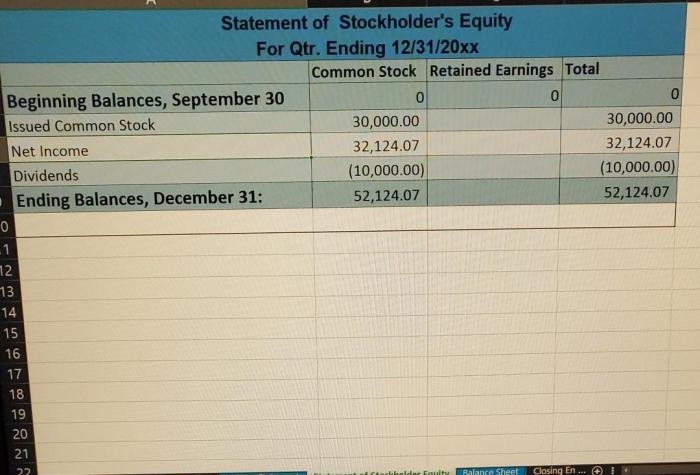
Financial statements are the primary means by which companies communicate their financial information to users. The three main financial statements are the balance sheet, the income statement, and the statement of cash flows.
Balance Sheet
The balance sheet provides a snapshot of a company’s financial position at a specific point in time. It shows the company’s assets, liabilities, and equity.
Income Statement
The income statement shows a company’s financial performance over a period of time. It shows the company’s revenues, expenses, and net income.
Statement of Cash Flows
The statement of cash flows shows a company’s cash inflows and outflows over a period of time. It shows how a company’s cash is being used.
Relationships Between the Financial Statements
The three financial statements are interrelated. The balance sheet shows the company’s financial position at a specific point in time, the income statement shows the company’s financial performance over a period of time, and the statement of cash flows shows how the company’s cash is being used.
Transaction Analysis

Transaction analysis is the process of analyzing business transactions to determine their effects on the financial statements. The first step in transaction analysis is to identify the accounts that are affected by the transaction. Once the affected accounts have been identified, the next step is to determine the amount of the transaction that should be recorded in each account.
Types of Transactions and Their Effects on the Financial Statements
- Revenue transactionsincrease a company’s assets and equity.
- Expense transactionsdecrease a company’s assets and equity.
- Asset transactionsincrease or decrease a company’s assets.
- Liability transactionsincrease or decrease a company’s liabilities.
- Equity transactionsincrease or decrease a company’s equity.
Examples of Transaction Analysis
- A company sells a product for $100. The transaction would increase the company’s assets by $100 and its equity by $100.
- A company pays $50 for rent. The transaction would decrease the company’s assets by $50 and its equity by $50.
- A company purchases a new machine for $1,000. The transaction would increase the company’s assets by $1,000 and its liabilities by $1,000.
Adjusting Entries
Adjusting entries are made at the end of an accounting period to ensure that the financial statements are accurate. Adjusting entries are used to record transactions that have occurred but have not yet been recorded in the accounting records. The most common types of adjusting entries are accruals and deferrals.
Accruals, Accounting 201 final exam cheat sheet
Accruals are adjusting entries that record expenses that have been incurred but have not yet been paid. For example, if a company has used $100 of supplies during the month but has not yet paid for them, an adjusting entry would be made to record the expense and the liability.
Deferrals
Deferrals are adjusting entries that record revenues that have been earned but have not yet been received. For example, if a company has received $100 for a service that will be performed in the next month, an adjusting entry would be made to record the revenue and the liability.
Examples of Adjusting Entries
- A company has used $100 of supplies during the month but has not yet paid for them. An adjusting entry would be made to record the expense of $100 and the liability of $100.
- A company has received $100 for a service that will be performed in the next month. An adjusting entry would be made to record the revenue of $100 and the liability of $100.
Closing Entries
Closing entries are made at the end of an accounting period to close the temporary accounts and transfer their balances to the permanent accounts. The temporary accounts are the income statement accounts and the expense accounts. The permanent accounts are the balance sheet accounts.
Steps Involved in Closing the Accounting Records
- Close the income statement accounts.
- Close the expense accounts.
- Transfer the balances of the income statement accounts and the expense accounts to the retained earnings account.
Examples of Closing Entries
- Close the revenue accounts.
- Close the expense accounts.
- Transfer the balance of the revenue accounts and the expense accounts to the retained earnings account.
Financial Ratios
Financial ratios are used to analyze a company’s financial performance. Financial ratios can be used to compare a company to its competitors, to track a company’s performance over time, and to identify potential problems.
Types of Financial Ratios
- Liquidity ratiosmeasure a company’s ability to meet its short-term obligations.
- Solvency ratiosmeasure a company’s ability to meet its long-term obligations.
- Profitability ratiosmeasure a company’s profitability.
- Efficiency ratiosmeasure a company’s efficiency.
Examples of Financial Ratios and Their Interpretation
- Current ratio:The current ratio measures a company’s ability to meet its short-term obligations. A current ratio of 2 or more is generally considered to be healthy.
- Debt-to-equity ratio:The debt-to-equity ratio measures a company’s ability to meet its long-term obligations. A debt-to-equity ratio of 1 or less is generally considered to be healthy.
- Gross profit margin:The gross profit margin measures a company’s profitability. A gross profit margin of 30% or more is generally considered to be healthy.
- Inventory turnover ratio:The inventory turnover ratio measures a company’s efficiency. An inventory turnover ratio of 1 or more is generally considered to be healthy.
Expert Answers: Accounting 201 Final Exam Cheat Sheet
What are the fundamental accounting concepts?
The fundamental accounting concepts include the accounting entity, going concern, monetary unit, periodicity, and materiality.
Why is it important to follow accounting standards?
Following accounting standards ensures consistency and comparability in financial reporting, allowing users to make informed decisions.
What are the three main types of financial statements?
The three main types of financial statements are the balance sheet, income statement, and statement of cash flows.