Cell organelles crossword answer key – Embark on a journey into the fascinating world of cell organelles with our comprehensive crossword answer key. Discover the intricate workings of these cellular components, their vital roles in cell function, and the evolutionary marvels that have shaped their existence.
From the enigmatic ribosomes to the powerhouse mitochondria, this guide provides a detailed exploration of the diverse range of cell organelles, their functions, and their intricate interactions.
Definition and Overview: Cell Organelles Crossword Answer Key
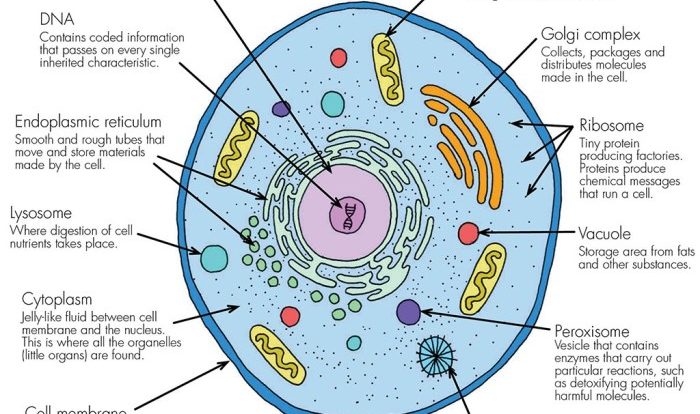
Cell organelles are specialized structures found within eukaryotic cells, which are cells of complex organisms such as animals, plants, and fungi. These organelles perform specific functions that are essential for cell survival and proper functioning.
Types of Cell Organelles
| Organelle | Function | Location | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nucleus | Contains genetic material | Center of cell | Membrane-bound organelle that houses the cell’s DNA and controls cellular activities. |
| Mitochondria | Produces energy | Cytoplasm | Double-membrane bound organelle responsible for cellular respiration and ATP production. |
| Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) | Protein synthesis and transport | Cytoplasm | Network of membranes that folds and transports proteins. Rough ER has ribosomes attached, while smooth ER lacks them. |
| Golgi Apparatus | Protein modification and packaging | Cytoplasm | Stack of flattened sacs that modifies, sorts, and packages proteins for secretion or storage. |
| Lysosomes | Digestion and waste disposal | Cytoplasm | Membrane-bound sacs containing digestive enzymes that break down cellular waste and foreign materials. |
| Peroxisomes | Detoxification and lipid metabolism | Cytoplasm | Small, membrane-bound organelles involved in detoxification and lipid metabolism. |
| Ribosomes | Protein synthesis | Cytoplasm and ER | Small, non-membrane bound organelles that assemble proteins using genetic information from mRNA. |
| Chloroplasts | Photosynthesis (in plant cells) | Cytoplasm | Green, double-membrane bound organelles that contain chlorophyll and perform photosynthesis in plant cells. |
Functions of Cell Organelles
- Nucleus:Houses genetic material (DNA), controls cellular activities, and directs protein synthesis.
- Mitochondria:Produces energy through cellular respiration, generating ATP.
- Endoplasmic Reticulum:Synthesizes, folds, and transports proteins. Rough ER also has ribosomes for protein synthesis.
- Golgi Apparatus:Modifies, sorts, and packages proteins for secretion or storage.
- Lysosomes:Digests cellular waste and foreign materials.
- Peroxisomes:Detoxifies harmful substances and participates in lipid metabolism.
- Ribosomes:Synthesizes proteins using genetic information from mRNA.
- Chloroplasts:Conducts photosynthesis in plant cells, converting sunlight into energy.
Cell Organelle Structure
Cell organelles have diverse structures that are adapted to their specific functions. The nucleus, for instance, is a spherical or oval organelle enclosed by a double membrane, known as the nuclear envelope. Inside the nucleus, chromatin, composed of DNA and proteins, is organized into structures called chromosomes.
Mitochondria are typically rod-shaped or oval organelles with a double membrane structure. The outer membrane is smooth, while the inner membrane is folded into numerous folds called cristae. These folds increase the surface area for energy production.
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) consists of a network of interconnected membranes that form flattened sacs and tubules. The rough ER has ribosomes attached to its surface, while the smooth ER lacks them.
The Golgi apparatus is a stack of flattened sacs called cisternae. These cisternae are surrounded by small vesicles that transport materials in and out of the Golgi.
Lysosomes are membrane-bound sacs that contain a variety of digestive enzymes. They are often spherical or oval in shape and range in size from 0.5 to 1.2 micrometers.
Peroxisomes are small, spherical organelles with a single membrane. They contain enzymes involved in detoxification and lipid metabolism.
Ribosomes are small, non-membrane bound organelles composed of RNA and proteins. They can be found either attached to the ER or free in the cytoplasm.
Chloroplasts are large, oval organelles found in plant cells. They are enclosed by a double membrane and contain a green pigment called chlorophyll, which absorbs sunlight for photosynthesis.
Cell Organelle Interactions
Cell organelles interact with each other in various ways to maintain cellular homeostasis and perform complex cellular functions. These interactions include physical connections, exchange of molecules, and coordinated regulation of activities.
For instance, the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and the Golgi apparatus work together in protein synthesis and secretion. The ER synthesizes proteins, which are then transported to the Golgi apparatus for modification, sorting, and packaging. The Golgi apparatus then releases the processed proteins into vesicles for secretion from the cell.
Mitochondria interact with other organelles to provide energy. They produce ATP, which is used by other organelles for cellular processes. In turn, mitochondria receive metabolites from other organelles, such as glucose from the cytoplasm and fatty acids from the ER, to generate ATP.
Lysosomes interact with other organelles to degrade cellular waste and foreign materials. They receive materials from the ER, Golgi apparatus, and other organelles, and break them down into smaller molecules that can be reused or excreted from the cell.
Cell Organelle Evolution
Cell organelles are believed to have evolved through a process called endosymbiosis. This theory suggests that certain organelles, such as mitochondria and chloroplasts, were once free-living bacteria that were engulfed by larger cells. Over time, these bacteria lost their ability to live independently and became integrated into the host cell as organelles.
Evidence supporting the endosymbiosis theory includes the presence of DNA in mitochondria and chloroplasts, as well as their similarity to free-living bacteria in terms of size, shape, and metabolic capabilities.
Applications of Cell Organelle Research
Research on cell organelles has led to numerous applications in medicine, biotechnology, and agriculture. Understanding the structure and function of organelles has helped researchers develop treatments for diseases that affect organelles, such as mitochondrial disorders and lysosomal storage diseases.
In biotechnology, cell organelle research has led to the development of techniques for manipulating organelles, such as gene editing in mitochondria. This has potential applications in treating genetic diseases and developing new therapies.
In agriculture, research on chloroplasts has helped improve crop yields by enhancing photosynthesis and resistance to environmental stresses. Understanding the mechanisms of chloroplast function has also led to the development of biofuels.
Detailed FAQs
What is the function of the Golgi apparatus?
The Golgi apparatus is responsible for modifying, sorting, and packaging proteins and lipids for secretion or storage.
How do mitochondria generate energy?
Mitochondria generate energy through a process called oxidative phosphorylation, which involves the transfer of electrons along an electron transport chain.
What is the role of the endoplasmic reticulum?
The endoplasmic reticulum is involved in protein synthesis, lipid synthesis, and detoxification.